One of the four main surgical patient positions, the lateral position is used for procedures that require surgical access to one side of the patient’s body. In the lateral position, the patient lies on one side. Some common procedures that may require a patient to be positioned in the lateral position include back surgeries, lower extremity surgeries, thoracic surgeries, Ear Nose Throat (ENT) surgeries, and kidney surgeries.
WHEN WOULD YOU PUT A PATIENT IN THE LATERAL POSITION?
The lateral position is used for surgical access to the thorax, kidney, retroperitoneal space, and hip.Depending on the side of the body on which the patient is being operated, the patient will lie on their left or right side. Before being placed in the lateral position, the patient is induced in the supine position. A team of Operating Room staff will then lift and turn the patient onto their nonoperative side. The patient is placed into the supine position toward the edge of the operative side of the surgical table and then turned onto the side toward the center of the table.
When positioning a patient in the lateral position, surgical staff should use safe practices and guidelines. The following are to be used as appropriate based on individual patient variables and the procedure. Surgical staff should refer to their facility's positioning policies and procedures for the safe positioning of patients.
- Place a pillow or head positioner under the patient’s head with the dependent ear assessed after positioning.
- Support and secure the patient’s arms on parallel armboards with one arm on each armboard and both arms abducted less than 90 degrees.
- Place an axillary roll under the patient’s dependent thorax, distal to the axillary fold, at the level of the seventh to the ninth rib.
- Verify the patient’s bilateral radial pulses after placement of the axillary roll.
- Maintain the patient’s physiologic spinal and neck alignment.
- Flex the patient’s dependent leg at the hip and knee. (This is done for extra support during the procedure, to reduce the risk of the patient tilting and falling.)
- Position the patient’s upper leg straight and support it with pillows between the legs.
- Place safety straps across the patient’s hips.
- Use lateral braces, kidney braces and bean bag positioners as needed.
As with all surgical positions, surgical staff should be aware of risks to the patient in the lateral position.
ALTERNATE POSITIONS TO THE LATERAL POSITION
Variations of the lateral position include lateral kidney position, lateral chest position, lateral sims recumbent position, and lateral jackknife position. The lateral kidney position is commonly used for kidney surgeries. Lateral chest position is used for unilateral transthoracic procedures.
With the assistance of lateral positioners, surgical teams can prepare patients effectively in side-lying positions before surgeries and operative procedures. HOWELL offers a variety of lateral positioners that will assist in positioning the patient on their side in either the right lateral or left lateral position, where the patient will have one side of their body touching the bed, with top leg over bottom leg, throughout the course of the procedure. Our selection of lateral patient positioners will ensure that patients maintain position comfortably, while keeping critical points of the body fully accessible by the surgeon on the OR table.
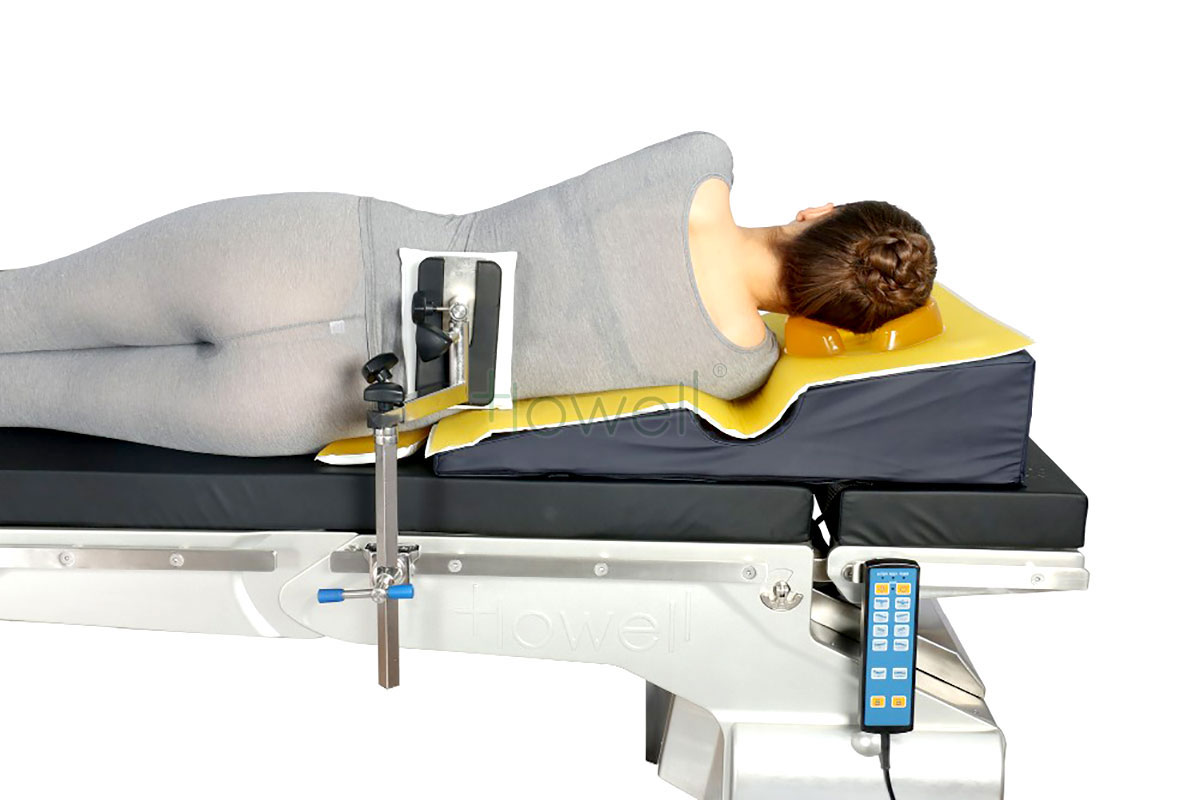
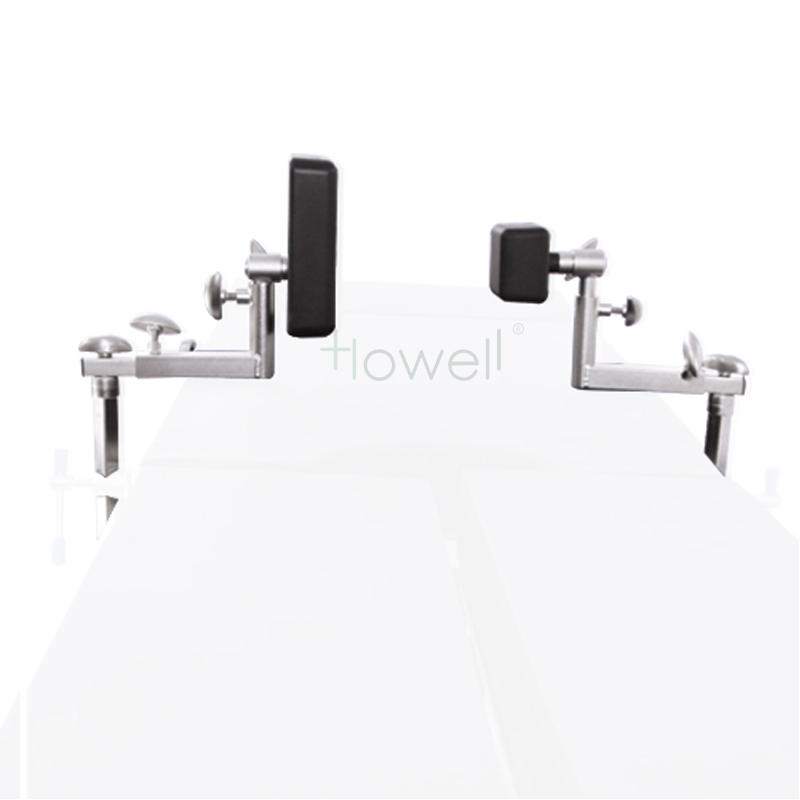 Lateral Positioner
Lateral Positioner – This positioner permits a safe, quick, and easy transition from the supine position to the lateral position. The patient’s lower shoulder fits into the integral channel to provide exceptional patient comfort and nerve protection while in the lateral position. The built-in headrest and axillary support assists in proper spinal alignment and surgical site access.

CONCLUSION
One of the four main patient positions, the lateral position provides access to the operative side of the patient’s body. Surgical staff should consider risks and complications associated with the lateral position such as pressure to structures of the dependent side of the body including the ears, shoulders, and ribs, brachial plexus injury, venous pooling, and diminished lung capacity.
Variations to the lateral position include the lateral kidney position, lateral chest position, and lateral jackknife position.
Regardless of what position is being used for a patient during a procedure, it’s important to follow best practices for positioning.


